This Python script demonstrates a simple client implementation for the Breeze Runtime software, allowing communication with the Breeze Runtime server for executing workflows and managing real-time data processing tasks. The client performs key operations such as connecting to the server, sending commands, listening for events, and streaming data. Below is an overview of the key functionalities:
-
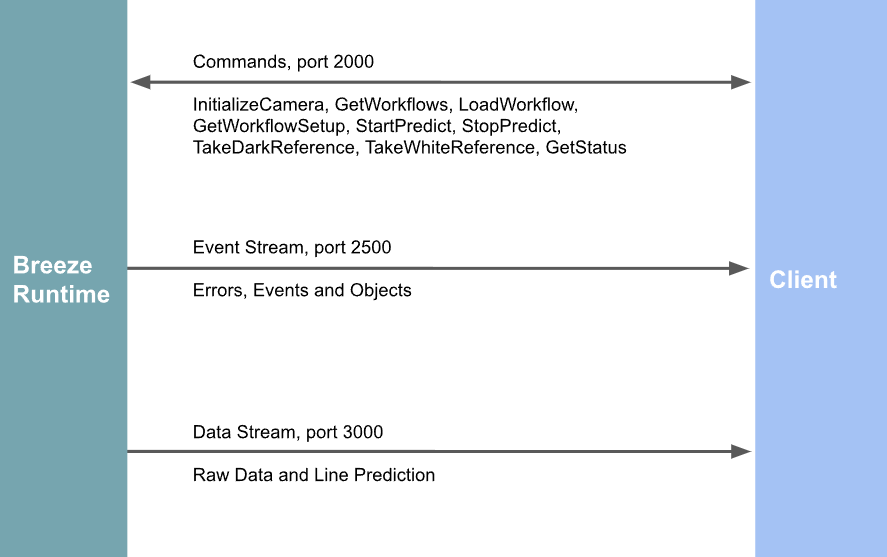
Server Connection: The client connects to the Breeze Runtime server using designated command, event, and stream ports, allowing communication for both command execution and event handling.
-
Command Execution: It sends various commands to the server (e.g., initializing the camera, loading a workflow, and starting/stopping predictions). Each command is sent with a unique identifier, and the client handles the server's responses, ensuring correct execution.
-
Event Stream Listening: The client listens for server events, such as prediction object data, and processes these in real-time. Event data is received in JSON format, parsed, and key information such as classification results is extracted and printed.
-
The field
CameraIdcan be used to detect the source of the event if multiple sensors are being used
-
-
Data Stream Listening: A separate thread listens for data streams from the server. The client parses the stream header to extract details such as stream type, frame number, and timestamps, allowing further processing of streamed data.
-
Each sensor (if multiple cameras are being used) has its own data stream starting at
Data Stream Portand adding one for each camera, e.g,-
First Camera (
CameraId = 0) -Data Stream Port = 3000 -
Second Camera (
CameraId = 1) -Data Stream Port = 3001
-
-
-
Workflow Management: The script loads a specific workflow (e.g., the Runtime Classification of nuts), takes dark and white references, and starts the prediction process on spectral data. The workflow path is dynamically constructed from the server's workspace property.
This client offers a foundation for integrating with the Breeze Runtime software, demonstrating how to handle real-time event and data stream processing for spectral analysis workflows.
import socket
import json
import uuid
import threading
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from dateutil import tz # python-dateutil - for time zone adjustment of dates
# Server host and port configuration
HOST = '127.0.0.1'
COMMAND_PORT = 2000
EVENT_PORT = 2500
DATA_STREAM_PORT = 3000
# Flag to control thread execution
stop_event = threading.Event()
def start_command_client():
soc = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
soc.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
soc.connect((HOST, COMMAND_PORT))
soc.settimeout(120)
return soc
def send_command(command_socket, command):
command_id = uuid.uuid4().hex[:8]
print(f"Sending command '{command.get('Command')}' with id {command_id}")
command['Id'] = command_id
message = json.dumps(command, separators=(',', ':')) + '\r\n'
command_socket.sendall(message.encode('utf-8'))
message_buffer = ""
while True:
try:
part = command_socket.recv(1024).decode('utf-8')
if not part:
break # Socket closed by the server
message_buffer += part
while '\r\n' in message_buffer:
full_response_str, message_buffer = message_buffer.split('\r\n', 1)
try:
response_json = json.loads(full_response_str.strip())
if response_json.get('Id') == command_id:
return response_json
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print(f"Invalid JSON received: {full_response_str}")
continue
except socket.timeout:
print("Request timed out")
return None
return None
def listen_for_events():
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as event_socket:
event_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
event_socket.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_TCP, socket.TCP_NODELAY, 1)
event_socket.connect((HOST, EVENT_PORT))
message_buffer = ""
while not stop_event.is_set():
event_socket.settimeout(1)
try:
data = event_socket.recv(1024).decode('utf-8')
if not data:
break
message_buffer += data
while '\r\n' in message_buffer:
message, message_buffer = message_buffer.split('\r\n', 1)
try:
message_json = json.loads(message)
event = message_json.get('Event', '')
inner_message = json.loads(message_json.get('Message', '{}'))
if event == "PredictionObject":
descriptors = inner_message.get('Descriptors', [])
start_date = convert_ticks_to_datetime(inner_message.get('StartTime', 0))
end_date = convert_ticks_to_datetime(inner_message.get('EndTime', 0))
start_line = inner_message.get('StartLine', 0)
end_line = inner_message.get('EndLine', 0)
camera_id = inner_message.get('CameraId', 0) # If multiple cameras are used
print(
f"start line:{start_line} end line:{end_line} start time:{start_date} end time:{end_date} classification:{descriptors[0]} cameraId:{camera_id}")
if (shape := inner_message.get('Shape')) is not None:
center_of_object = [int(coord) for coord in shape.get('Center', [])] # [X,Y]
border_of_object = [[int(coord) for coord in point] for point in shape.get('Border', [])] # [[X,Y]..]
# print(f"shape - center:{center_of_object} border:{border_of_object}")
# NOTE: Quite a verbose output
else:
print(f"event:{event} message:{inner_message}")
except json.JSONDecodeError:
print("Invalid JSON received")
except socket.timeout:
continue
def listen_for_data_stream():
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as stream_socket:
stream_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
stream_socket.setsockopt(socket.IPPROTO_TCP, socket.TCP_NODELAY, 1)
stream_socket.connect((HOST, DATA_STREAM_PORT))
expected_header_size = 25 # 1 + 8 + 8 + 4 + 4 bytes = 25 bytes
while not stop_event.is_set():
stream_socket.settimeout(1)
try:
header = b""
# Ensure that the full header is received
while len(header) < expected_header_size:
chunk = stream_socket.recv(expected_header_size - len(header))
if not chunk:
break # connection closed
header += chunk
if len(header) != expected_header_size:
print("Incomplete header received")
continue
# Manually parse the header
stream_type = header[0]
frame_number = int.from_bytes(header[1:9], byteorder='little', signed=True)
timestamp = int.from_bytes(header[9:17], byteorder='little', signed=False)
metadata_size = int.from_bytes(header[17:21], byteorder='little', signed=False)
data_body_size = int.from_bytes(header[21:25], byteorder='little', signed=False)
# Print the parsed values
print(f"Stream Type: {stream_type}, Frame Number: {frame_number}, "
f"Timestamp: {timestamp}, Metadata Size: {metadata_size}, Data Body Size: {data_body_size}")
# Skip metadata and data body based on their sizes
stream_socket.recv(metadata_size)
stream_socket.recv(data_body_size)
except socket.timeout:
continue
def convert_ticks_to_datetime(ticks):
return (datetime(1, 1, 1) + timedelta(microseconds=ticks // 10)).replace(tzinfo=tz.tzutc()).astimezone(tz.tzlocal())
def handle_response(response):
if not response:
raise ValueError(f"No response or incorrect response ID received: {response}")
message = response.get('Message', '')
if not response.get("Success", False):
raise RuntimeError(f"Command not successful: {message}")
print(f"Id: {response.get('Id')} successfully received message body: '{message[:100]}", end="")
if len(message) > 100:
print("...", end="")
print("'")
return message
def main():
with start_command_client() as command_socket:
handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "InitializeCamera"}))
# Get current Breeze workspace path
ws = handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "GetProperty", "Property": "WorkspacePath"}))
# This is using the tutorial default workflow from nuts tutorial
# see https://help.prediktera.com/breeze-runtime/runtime-classification-of-nuts
workflow_path = f"{ws}/Data/Runtime/Nuts_Classification.xml"
handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "LoadWorkflow", "FilePath": workflow_path}))
handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "TakeDarkReference"}))
handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "TakeWhiteReference"}))
handle_response(send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "StartPredict", "IncludeObjectShape": True}))
event_listener_thread = threading.Thread(target=listen_for_events)
data_stream_listener_thread = threading.Thread(target=listen_for_data_stream)
event_listener_thread.start()
data_stream_listener_thread.start()
input("Press Enter to stop prediction...\n")
try:
response = send_command(command_socket, {"Command": "StopPredict"})
handle_response(response)
except (ValueError, RuntimeError) as e:
print(f"Error during stop prediction: {e}")
finally:
stop_event.set()
event_listener_thread.join()
data_stream_listener_thread.join()
print("Done")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
